Basically wargames are providing the basic knowledge on the security concepts. It is a game that contain many tricks to break the borders to gain the access especially passwords (commands are mostly on the Linux CLI). You can find many wargames through the Internet and they are very interest and fun full too. “Bandit” is also a wargame which is for the beginners. You all can access that through the link given bellow. And this article is an document for this game. I have used Ubuntu as the operating system.
Case study → Clickhere
Here we have need to connect the host through the SSH (secure socket shell) server. The informations are provided as follows.
Host name: bandit.labs.overthewire.org
Port No: 2220
User name: bandit0
Password: bandti0
There are many ways to connect through the SSH server.
Method 1:
Download and run the “PuTTY SSH client”. (https://the.earth.li/~sgtatham/putty/latest/w64/putty.exe)
Method 2:
By using terminal (ctrl+alt+T). [ssh bandit.labs.overthewire.org -p 2220 -l bandit0]
-p → for the port no
-l → for the user name
Note:
1.When typing the password in terminal that will not be appear. Just type it and press enter.
2. This documentation is using the “Method 2” which is mentioned above
Level 0-1:
Case study → Clickhere.
1. Make sure that we are in the home directory. [pwd]
2. List the files inside that directory. [ls]
3. Read the file “readme”. [cat readme]
Level 1-2:
Case study → Clickhere.
Username : bandit1
Password: boJ9jbbUNNfktd78OOpsqOltutMc3MY1
1. Make sure that we are in the home directory. [pwd]
2. List the files/directories inside that location. [ls]
3. Read the file “-”.
Here [cat -] will not work, because the “-”filename can not be read directly by the [cat] command. Therefore we have need to say the shell to execute this file, that can be done in 2 ways.
[cat ./-] → [./] execute the file in the present directory
[cat /home/bandit1/-] → giving the absolute path for the file to execute
Level 2-3:
Case study → Clickhere.
Username: bandit2
Password: CV1DtqXWVFXTvM2F0k09SHz0YwRINYA9
1. Make sure that we are in the home directory. [pwd]
2. List the files/directories inside that location. [ls]
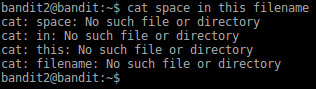
3. Read the file “spaces in this filename”.
Here if we type the file name after [cat] command as like this [cat spaces in this filename], we will get some errors because of it space characters.
To avoid that
[cat spaces\ in\ this\ filename] → [\] this is considered as escape sequence. Don’t consider the inbetween space
[cat “spaces in this filename”] → by providing the name as a one string by using quotations
Level 3-4:
Case study → Clickherehttp://overthewire.org/wargames/bandit/bandit4.html
Username: bandit3
Password: UmHadQclWmgdLOKQ3YNgjWxGoRMb5luK
1. List the files/directories inside that location. [ls]
2. List the hidden files inside the “inhere” directory. [ls -al inhere/]
-a → show hidden files
-l → list the files and directories inside the given path with permissions + links + owner + groups + size + time + name
3. Read the hidden file. [cat inhere/.hidden]
Level 4-5:
Case study → Clickherehttp://overthewire.org/wargames/bandit/bandit5.html.
Username: bandit4
Password: pIwrPrtPN36QITSp3EQaw936yaFoFgAB
Here we can find the solution by 2 methods.
Method 1:
By opening and see the content in the file name.
1. List the files/directories inside that location. [ls]
2. Move inside the “inhere” directory. [cd inhere/]
3. List the files/directories inside that location. [ls]
4. Read each file contents. [cat ./-file00]
It will take long step to encounter this stage, because there are 10 files needs to read.
Method 2:
By using [xarg] we can find the correct file and open that file.
1. List the files/directories inside that location. [ls]
2. Move inside the “inhere” directory. [cd inhere/]
3. List the files/directories inside that location. [ls]
4. Find the file which is contain human readable text (ASCII).
[find ./ |xargs file| grep text] or [find /home/bandit4/inhere/ |xargs file| grep text]
[xargs] → helps to execute find function for many files
[grep] → pick the file which is contain text characters.
[|] → redirects the output of the first as the input of the second.
Level 5-6:
Case study → Click here. (http://overthewire.org/wargames/bandit/bandit6.html)
Username: bandit5
Password: koReBOKuIDDepwhWk7jZC0RTdopnAYKh
1. Move inside the “inhere” directory. [cd inhere/]
2. List the files/directories + sub-folders + hidden files
inside that location. [ls -alR]
-R → display the sub folders and files
pic_12.png
Here the file is want to be a human readable, size 1033 bytes
and it can’t be executable. We can checks these conditions in many ways.
Method 1:
By using [ls] we can find the filename
[ls -alR | grep -b 1033] – check the file which is matching
to the size of 1033.
-b → byte offset
Here we cannot see the parent directory of the file but when
looking the access permission we can make sure that file is executable or not.
[ls -alR | grep -B10 1033] – it will print the matching file
with some file which are inside the same directory
-B → there should be a number value after this. [-B10 1033] –
print 10 lines contain this matching byte size 1033.
pic_13.png
Method 2:
By using the [find] command
[find /home/bandit5 -size 1033c -readable -type f] – it will
display the file name with absolute path for the matching files
pic_14.png
[-size 1033c] → file size is 1033 byte . Type [man find] and
you can be able to see the attributes that can be use for the find commands.
Pic_15.png
To read the file we can use [cat] command.
Level 6-7:
Case study → Click here. (http://overthewire.org/wargames/bandit/bandit7.html)
Username: bandit6
Password: DXjZPULLxYr17uwoI01bNLQbtFemEgo7
©IT Today











Comments
Post a Comment